If you are as serious as Jayson Marwaha about making your charitable contributions count, here’s the journey you’d make: One day as a Virginia high school student you’d load a surplus urinalysis machine that you salvaged from a local manufacturer into your parents’ minivan for delivery to a free clinic in Maryland. By your junior year of college you’d dedicate your entire 2013 spring break to installing a custom-developed medical device inventory and repair management software system on the servers of the Zanzibar Ministry of Health.
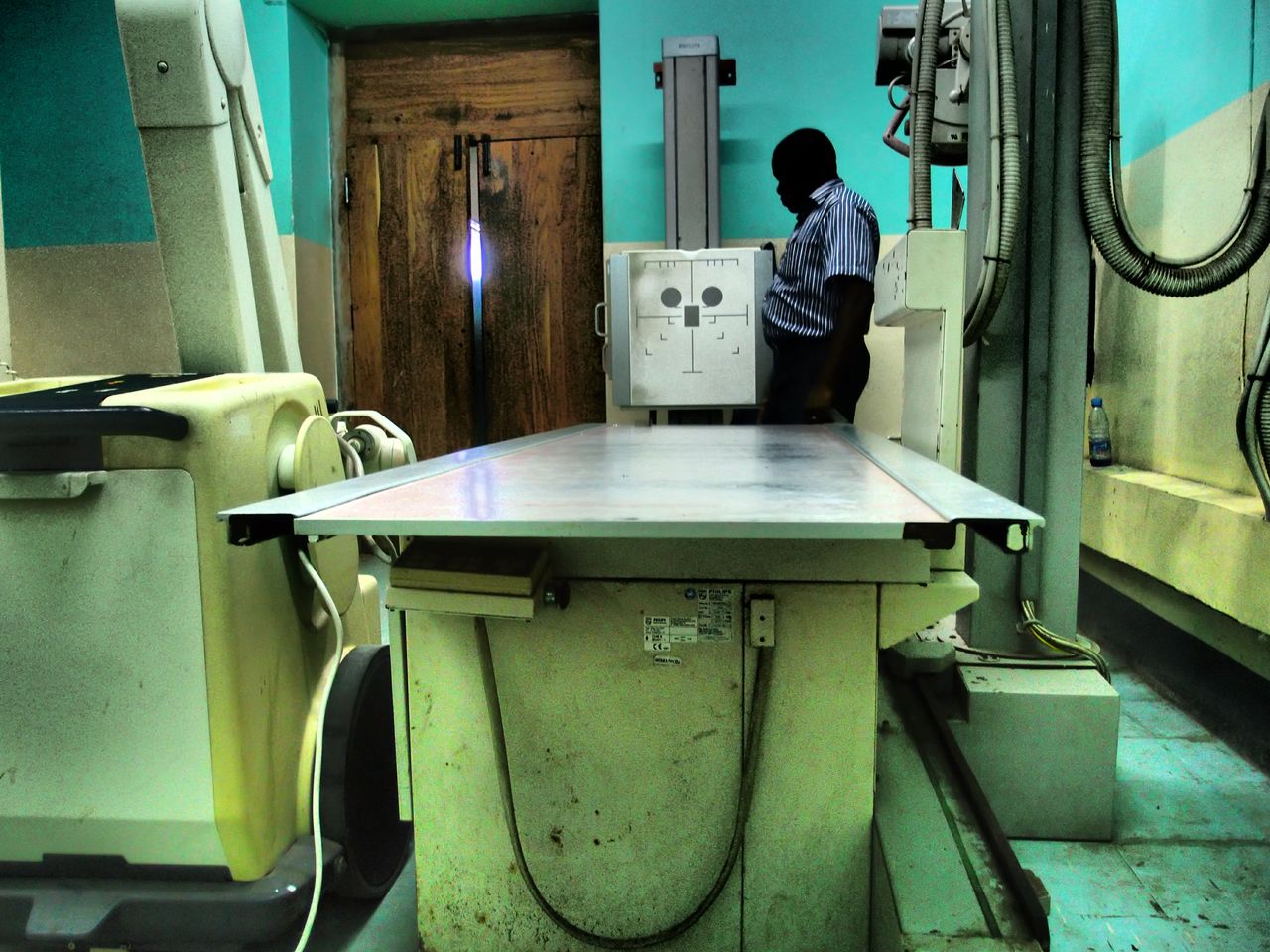

Along the way you’d have built a nongovernmental organization called MED International into a team of eight Brown University and one Boston Univeristy student volunteers and a professional engineer under contract in Zanzibar. In partnership with the local government, your team’s work would help fix more than $50,000 worth of the most needed equipment in three hospitals there. Your NGO would arrange donations of genuinely needed equipment, but the team would also perform a systematic needs assessment and help local engineers develop the management software. The engineer employee you’ve hired full-time for six months with the money you’ve raised would start teaching courses at the local college to train technicians in electronics and repair.
What connects Maryland to Zanzibar in Marwaha’s journey is his acquired wisdom that well-intentioned giving is no match for intimately understanding his beneficiary’s needs and doing whatever it takes to build their underlying capacity. Marwaha learned this when he followed up on that urinalysis machine in Maryland a few months after the minivan trip. The woman on the other end of the phone told him that the clinic, which at first seemed glad to accept the machine, had since gotten rid of it. They didn’t do urinalysis and didn’t have the staff to operate it.
“That was really the point at which I realized the donation methodology was flawed,” Marwaha said during a Skype interview from Zanzibar. “It shouldn’t be supply-driven, in that I pick up whatever I can and send it to whoever says yes. It should be demand-driven in that you first think about what the need is and then you source equipment appropriately.”
From van to venture
After that lesson in the ad hoc minivan days of 2009, Marwaha began to realize that if he wanted to make a real and lasting impact internationally, he’d need to find a beneficiary who would be a long-term partner. In 2011, he started calling African embassies in search of such a deep and productive relationship. Malawi, Tanzania, and Rwanda all expressed interest, but a Zanzibari native in the Tanzanian embassy went so far as to set up a meeting in October for Marwaha with a delegation from the island region led by Vice President Seif Ali Iddi.
By then Marwaha was at Brown. He realized he’d need help if he was to sustain the serious partnership he had forged. He had begun working with Alan Harlam at the Swearer Center, which made it easier to reach out to fellow students.
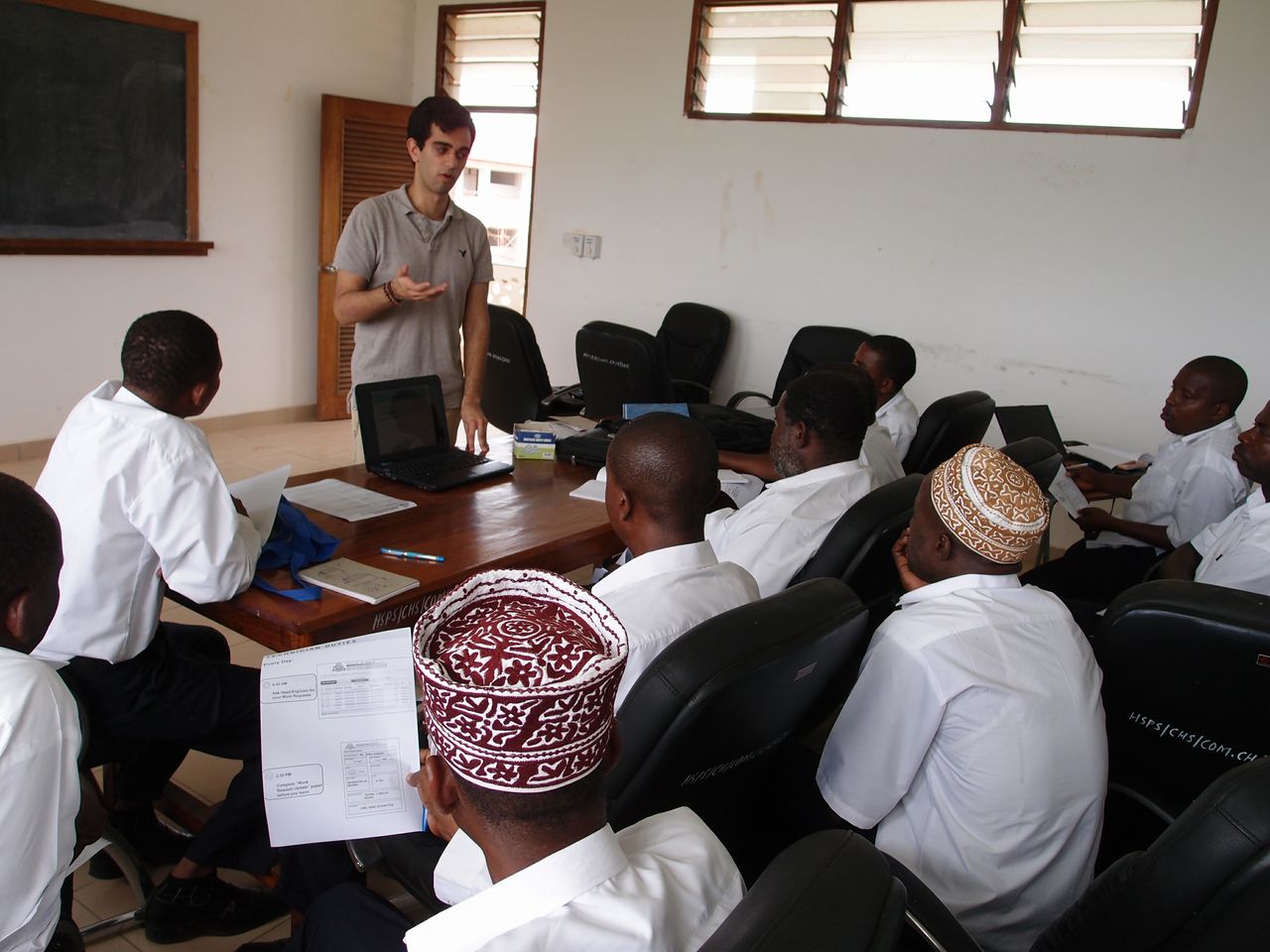

Help came in the person of Han Sheng Chia. Now the co-executive director, Chia is a Singapore native and political science junior whose previous international relief experience included a benchmarking analysis of best practices among orphanages in Nepal. Chia and Marwaha went to Zanzibar in the summer of 2012 and performed a needs assessment and inventory of three hospitals on the islands. They presented the report to the health ministry at the end of August with a focus on three main problems to remedy: “Weak Equipment Management Procedures,” “Low Repair Capacity,” and “Donations are Not Relevant/ Matched to Zanzibar’s Needs.”
The solution was to keep adding people with the right expertise. Computer science concentrator Ryan Chan helped to develop software with the Tanzanian health ministry that will establish a workflow between the medical and engineering staff at three hospitals for equipment repair. It will also allow the health ministry to share their equipment needs with donors all over the world.
And by hiring engineer Kevin McCracken, who began volunteering last summer, both as a technician and an instructor, MED International is improving the region’s repair capacity.
MED International’s help is definitely welcome, said Juma Hamad, chief engineer for the health ministry’s health care engineering unit.
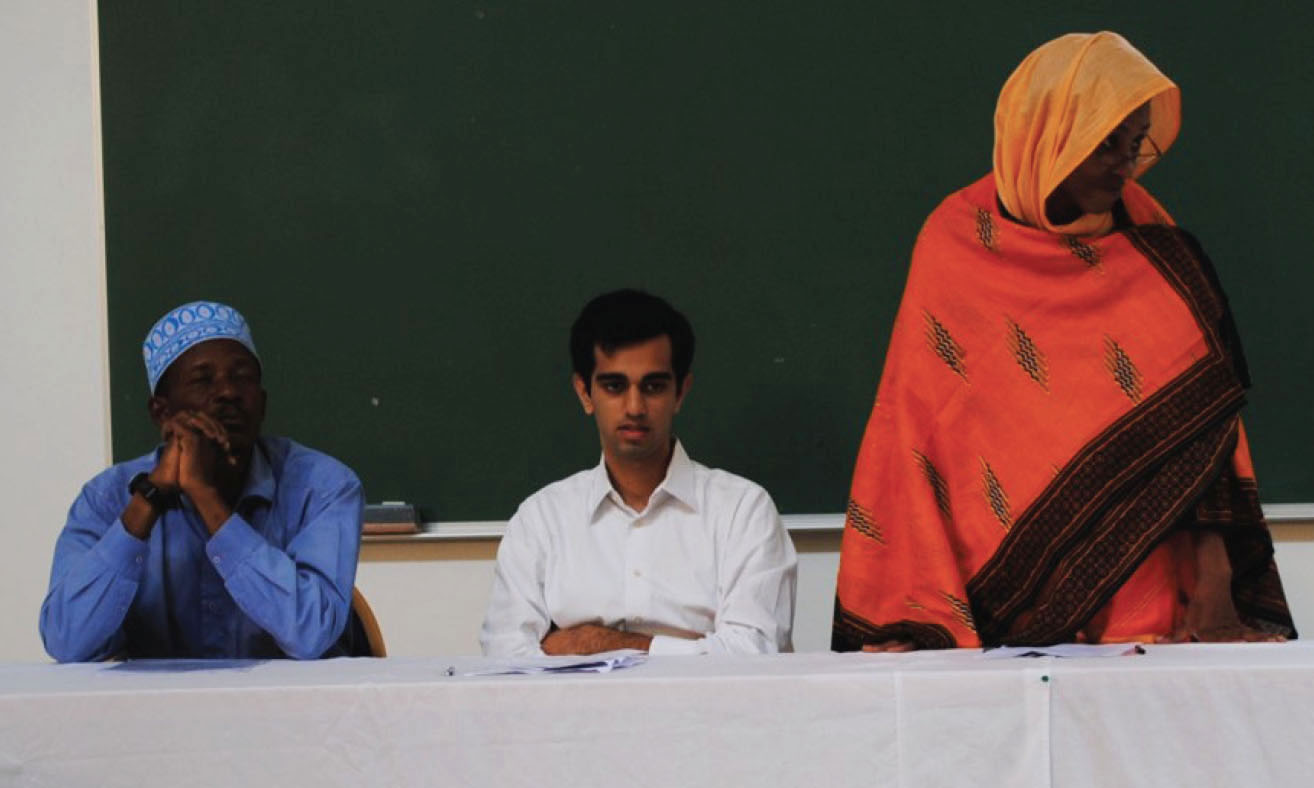

“It’s a blessing for us to have MED International with us,” Hamad said. “They are helping us on so many fronts. We have the medical equipment management within the ministry of health really helping us because we were develolping our software and they came here and helped us a lot. They are helping us with running the course at the college of health sciences.”
Based at Brown
MED International’s ability to help Zanzibar derives from the help its supporters provide. The University, along with other sponsors, has helped finance the effort and both Harlam and global health faculty members Susan Cu-Uvin and Michael Koster have provided advice. More help has come from offices as diverse as the School of Engineering, Human Resources, and Purchasing, Han said.
More than anything else, the University’s diverse pool of student talent is what has allowed the organization the social science, technological, and medical versatility to take on the challenges it has found.
It’s been a while since Marwaha’s mission was just about donating available equipment. As Chia puts it, “We are a problem solving organization.”
MED International will engage the Brown community more broadly on Friday, April 5, at 8 p.m., with a music-infused fundraiser called “Heart Beats.” Chia will deliver a presentation about the group’s work, but the program also promises a “a stunning lineup of singing professors,” including Barrett Hazeltine, Alan Harlam and Bill Allen.
Whatever additional support they can garner will help MED International persevere with a model that Marwaha hopes he can expand further.
“On the ground we are piloting the efficacy in two hospitals and a public health lab,” he said. “Once the efficacy is proved we will diversify within Zanzibar and beyond.”
From Chief Engineer Hamad’s standpoint, it seems likely they’ll succeed.
“We quite appreciate what they are doing here in Zanzibar,” he said. “We know they have limited funds, but they are quite serious about what they are doing.”
It’s a seriousness born of having learned what how far one should go to truly help.